Internet Protocol Television
IPTV
What is IP TV?
IP TV stands for Internet Protocol Television, i.e., television that is delivered to the house over an IP Network, rather than over traditional satellite, cable or terrestrial networks. This means that the television content is packetized into IP packets and delivered through a high speed access network (like Digital Subscriber Line ( DSL)).
The term IPTV should not be confused with the delivery of television over internet (for example watching YouTube videos or live channels like NDTV on your PC over your broadband connection). Traditionally internet is a best effort network and does not provide any guarantees to an individual service. However, the IP network used for delivery of IPTV is built specially to deliver this service and hence has performance and security features required to build a reliable service which customers will pay for.
Hence, IPTV is usually provided by fixed network providers who already deliver voice and internet services to the last mile (i.e., the customer premises), and have control over the network from the head end up to the customer premise. Traditional TV using satellite or cable only includes Live TV and maybe a fixed small collection of movies that can be viewed as pay per view. IPTV is typically richer with features like gaming, time shift television and Video on Demand (VoD), apart from live TV. More on these features are described in the FAQ.
History
The term IPTV first appeared in 1995 with the founding of Precept Software. Precept developed an internet video product named IP/TV. It was a Windows and Unix-based application that transmitted single and multi-source audio and video traffic, ranging from low to DVD quality. Precept was acquired by Cisco Systems in 1998. Cisco retains the IP/TV trademark.
Kingston Communications, a regional telecommunications operator in the UK, launched KIT (Kingston Interactive Television), an IPTV over DSL broadband interactive TV service in September 1999. Kingston was one of the first companies in the world to introduce IPTV and IP VoD over ADSL.[1]
How does it work?
The figure below gives a very high level view of an IPTV system.
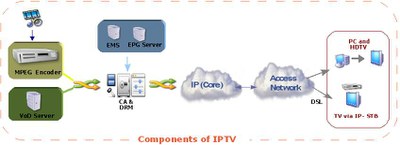 |
|---|
Figure 1: IPTV High level Architecture[2]
At the head end, content like Live TV channels are picked up from various sources like the satellite, and decrypted. The content is then compressed into a digital format like MPEG-2 or MPEG-4. Multiple programs or channels or sources like this are then packed into a single transport stream (MPEG2-TS) and packetized into IP packets to be multicast over the IP network.
Video on Demand programs are stored in a VoD Server after encrypting them with content protection mechanisms. The VoD servers are either centralized or geographically distributed. The VoD content is accessed by the individual subscriber through a unicast stream, since it is on-demand, catering to one individual.
The IP packets reach the home through a broadband access like DSL, where a splitter is used to separate out the TV from regular broadband.
The TV channels are played out through the Set Top Box, which is programmed to listen to the multicast channels depending on which channel it is tuned to, or the unicast stream for video on demand. It provides the interactive interface to allow the user to navigate different live channels, Video on Demand, movies, games, etc.
In the case of multiple set top boxes and PCs to view the programs, a home gateway can be used. Protocols like DLNA are used for networking within the home.
IPTV viewing on the PC
Viewing IPTV content on a Personal Computer usually requires a client which allows protected content to be viewed, and to provide a TV like view with programming guides, etc. Verimatrix Viewright is an example of a PC client that decodes protected content for PC viewing. More about this will be discussed in Module 8.2 IPTV.
IPTV viewing on cable
This will be discussed in detail in Module 8.7 Cable TV.
IPTV in India
In India, IPTV services are provided by Bharti Airtel in Delhi and Bangalore, as well as by BSNL and MTNL (through Aksh Optifiber (branded as iControl) and Smart TV group (branded as MyWay)). MyWay has recently exited the IPTV market due to insufficient demand.[3] IPTV is expected to pick up again in a few years when there is better last mile connectivity with Fiber to the Home (FTTH) or Long Term Evolution (LTE).
[1].From Wikipedia (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IPTV)
[2].HSC Technical Wiki (bit.ly/ND9zxt)
[3].Light Reading Article (http://bit.ly/uKDGdG)